Spider Veins vs. Varicose Veins: What’s the Difference?
Spider veins and varicose veins are common vascular conditions that, while often used interchangeably, have distinct characteristics, causes, and treatment options. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective management and treatment.
Thursday, 23 March, 2025
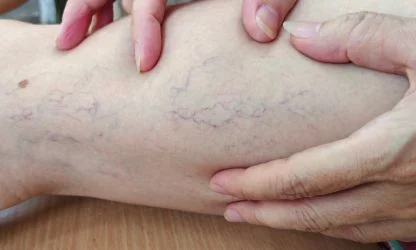
What Are Spider Veins?
Spider veins, medically known as telangiectasias, are small, dilated blood vessels that appear near the surface of the skin. They are typically red, blue, or purple and resemble a spider's web or tree branches. Commonly found on the legs and face, spider veins are usually asymptomatic and are primarily a cosmetic concern.
What Are Varicose Veins?
Varicose veins are larger, swollen veins that often appear twisted and bulging, resembling cords beneath the skin. They are most commonly found on the legs, particularly the calves, back of the legs, or inside the thighs. Unlike spider veins, varicose veins can cause discomfort, including heaviness, aching, or pressure in the affected limbs.
Causes and Risk Factors
Both conditions result from weakened or damaged valves in the veins, leading to blood pooling and vein enlargement. However, the contributing factors include:
-
Genetics: A family history of vein problems increases the risk.
-
Age: The risk of developing these vein issues increases with age.
-
Gender: Women are more susceptible due to hormonal influences, especially during pregnancy, menopause, or when taking birth control pills.
-
Occupation: Jobs requiring prolonged standing or sitting can contribute to vein problems.
-
Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity and obesity can increase pressure on veins.
Causes and Risk Factors
Both conditions result from weakened or damaged valves in the veins, leading to blood pooling and vein enlargement. However, the contributing factors include:
-
Genetics: A family history of vein problems increases the risk.
-
Age: The risk of developing these vein issues increases with age.
-
Gender: Women are more susceptible due to hormonal influences, especially during pregnancy, menopause, or when taking birth control pills.
-
Occupation: Jobs requiring prolonged standing or sitting can contribute to vein problems.
-
Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity and obesity can increase pressure on veins.
Symptoms
-
Spider Veins: Generally asymptomatic but may occasionally cause mild discomfort or itching.
-
Varicose Veins: Can cause aching pain, heaviness, throbbing, muscle cramping, swelling, and itching. In severe cases, they may lead to skin ulcers or blood clots.
Diagnosis
A physical examination by a healthcare provider is typically sufficient to diagnose spider and varicose veins. For varicose veins, especially if complications are suspected, an ultrasound may be performed to assess blood flow and rule out deeper vein issues.
Treatment Options
Treatment varies based on the severity and symptoms:
-
Lifestyle Changes: Regular exercise, weight management, elevating legs, and avoiding prolonged standing or sitting can alleviate symptoms and prevent progression.
-
Compression Therapy: Wearing compression stockings helps improve blood flow and reduce swelling.
-
Sclerotherapy: A minimally invasive procedure where a solution is injected into the affected veins, causing them to collapse and fade. Effective for both spider veins and small varicose veins.
-
Laser Treatments: Non-invasive laser therapies use light energy to eliminate spider veins and small varicose veins.
-
Endovenous Ablation Therapy: Uses heat, such as radiofrequency or laser, to close off larger varicose veins.
-
Surgical Options: In severe cases, procedures like vein stripping or ligation may be necessary to remove or tie off affected veins.
Prevention
While not all vein issues are preventable, certain measures can reduce the risk:
-
Exercise Regularly: Promotes healthy blood circulation.
-
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Reduces unnecessary pressure on veins.
-
Elevate Legs: Periodically elevating your legs can improve circulation.
-
Avoid Prolonged Sitting or Standing: Take breaks to move around and stretch.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience significant discomfort, swelling, skin changes, or ulcers near the affected veins, it's essential to consult a healthcare provider. These could be signs of chronic venous insufficiency or other complications requiring medical intervention.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between spider veins and varicose veins is vital for effective management and treatment. While spider veins are primarily a cosmetic concern, varicose veins can lead to discomfort and more serious health issues if left untreated. Consulting with a vascular specialist can provide personalized treatment options to improve vein health and overall quality of life.